What is Moltbot? - Complete Guide to the Self-Hosted AI Assistant (2026)
Moltbot (formerly Clawdbot) is a viral, open-source personal AI assistant created by Peter Steinberger. Its name is a play on Claude (the AI model it often uses) and its lobster mascot.
Unlike standard chatbots, Moltbot functions as a persistent agent that runs 24/7 on your local machine, acting as a "Personal OS" that can actually do things.
Important Rebrand to 'Moltbot'
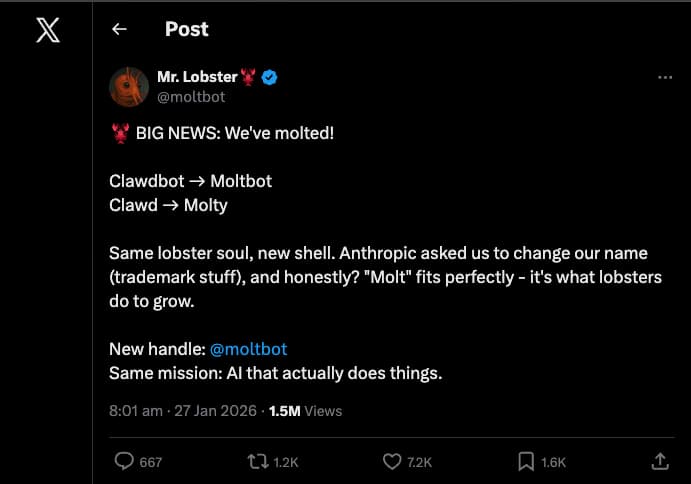
On 27 January 2026, the project rebranded to Moltbot after a trademark request from Anthropic (the makers of Claude). The creators noted that "molting" is a fitting metaphor for how lobsters grow and evolve.
The Woebot Era:
Before Clawdbot, the project was briefly known as Woebot. After a cease-and-desist from Anthropic regarding the name, it transitioned to Clawdbot, before finally landing on Moltbot to fully distance itself from the "Claude" trademark while keeping the crustacean identity.
CRITICAL SECURITY WARNING
The original Clawdbot GitHub account and Twitter/X handle (@clawdbot) were compromised by crypto scammers during the rebrand process. These accounts now post fake token sales and phishing links.
- Do NOT visit the old
github.com/clawdbotrepository - Do NOT interact with
@clawdboton Twitter/X - The official new handles are @moltbot and github.com/moltbot
If you previously starred or cloned the old repository, update your bookmarks immediately.

"Same lobster soul, new shell." — The Moltbot Team
The name change marks a significant step in the project's maturity, separating its identity from the underlying model provider while keeping the beloved crustacean theme.
For a detailed comparison of what changed between Clawdbot and Moltbot, see the comprehensive guide: Moltbot vs Clawdbot: Everything You Need to Know
The Genesis of Ambient Agency
The emergence of Moltbot represents a significant inflection point in the historical trajectory of artificial intelligence, marking a transition from reactive, web-boxed tools to proactive, ambient agents that inhabit the user's primary communication layer.
For the better part of the last decade, consumer interaction with large language models has been defined by the "destination model," wherein a user must navigate to a specific website or application, initiate a session, and engage in a transient exchange of information that rarely survives the closing of a browser tab. Moltbot fundamentally disrupts this cycle by repositioning the assistant within messaging applications such as WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, and iMessage.
The Problem of AI Fatigue
"Modern users suffer from 'AI fatigue'—the cognitive load required to manage multiple siloed tools, copy-paste outputs, and re-establish context for every new interaction."
By existing where users already communicate, Moltbot transforms the assistant from a tool into a persistent presence—a "24/7 Jarvis" that possesses long-term memory and the capability to execute real-world tasks.
Unlike traditional assistants like Siri, which have historically struggled with context and execution, Moltbot operates as an agentic system, meaning it can autonomously plan and execute multi-step actions without continuous human prompting. This shift is not merely cosmetic; it represents a fundamental change in how digital agency is constructed, stored, and executed.
Moltbot Architecture: Deep Dive
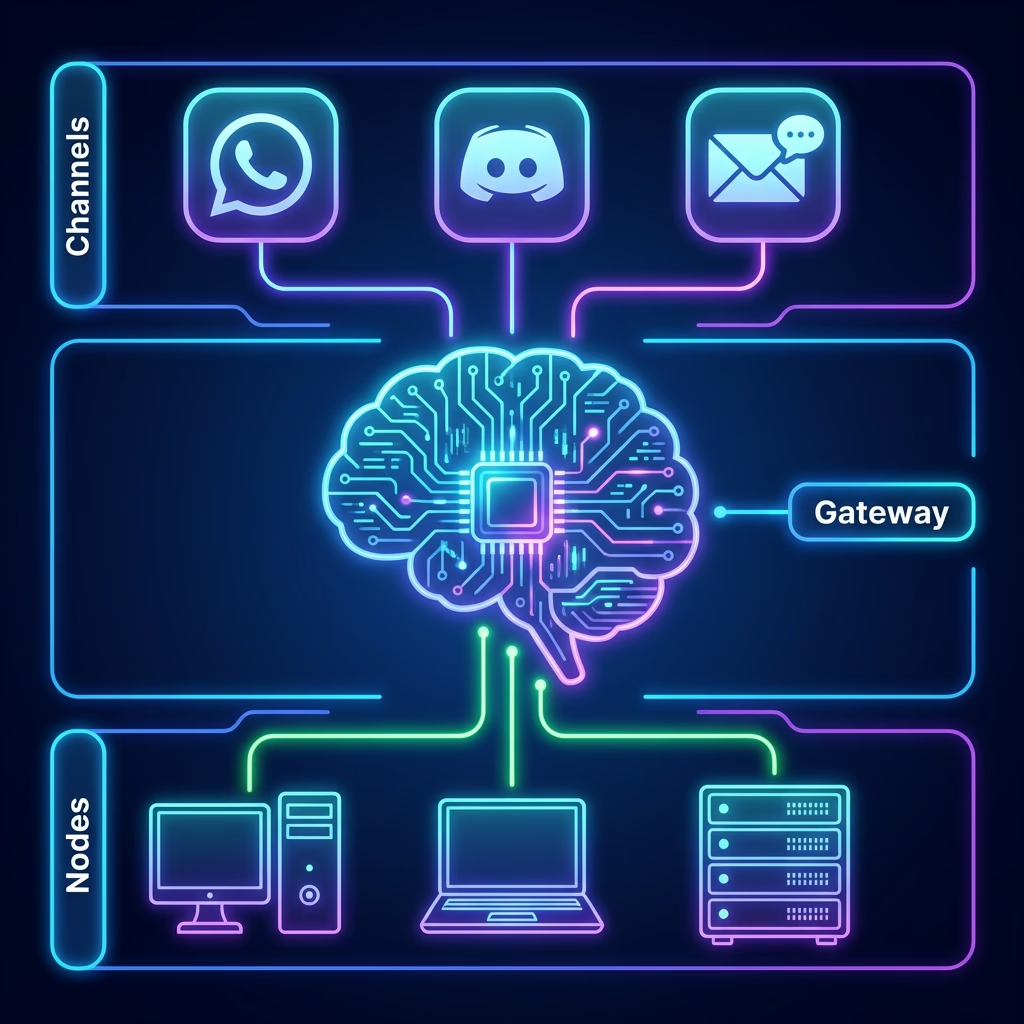
The operational efficacy of Moltbot is derived from a modular, three-tier architecture comprising the Gateway, the Nodes, and the Skills. This separation of concerns allows the system to bridge the gap between high-level reasoning—provided by frontier models like Anthropic's Claude—and local system execution.
The Gateway and Control Plane
At the center of the ecosystem is the Gateway, a long-running process that acts as the single source of truth for all channel connections, session states, and tool routing. The Gateway typically runs as a background service on Node.js 22 or higher, exposing a WebSocket control plane and a local HTTP interface for the browser-based Control UI.
It serves as the switchboard that translates incoming messages from messaging platforms into standardized prompts for the large language model and conversely routes the model's outputs or tool calls back to the appropriate channel.
| Component | Primary Responsibility | Technical Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Gateway | Routing, Session Management, Model Interfacing | Node.js, WebSockets, SQLite |
| Nodes | Hardware Access, Local Execution, File I/O | TypeScript, Swift, Kotlin |
| Channels | Multi-platform Integration (WhatsApp, Discord, etc.) | Baileys, grammY, Discord.js |
| Skills | Extensible Automation and Toolsets | Markdown (SKILL.md), Shell Scripts |
Distributed Nodes and Local Resource Access
While the Gateway handles the logic, the Nodes provide the execution environment. A Node is a process that gives the assistant access to the host machine's resources, including the file system, browser automation, microphone, camera, and platform-specific APIs.
This architecture supports distributed execution; a Gateway running on a cloud server can command a Node running on a local Mac Mini to perform device-specific actions, such as sending an iMessage or capturing a screenshot. This capability is critical for achieving "Jarvis-level" integration, where the assistant can bridge the divide between digital communication and physical hardware control.
Multi-Channel Messaging Integration
The system's primary interface is the messaging layer, which supports an expansive array of platforms. This multi-channel approach ensures that the same conversation, memory, and context follow the user across their entire device ecosystem.
| Interface Category | Supported Channels |
|---|---|
| Mainstream Messaging | WhatsApp, Telegram, iMessage, Signal |
| Professional/Collaborative | Slack, Discord, Microsoft Teams, Google Chat |
| Specialized/Regional | Matrix, Zalo, BlueBubbles |
| Direct/Internal | WebChat, CLI, macOS/iOS/Android Apps |
The integration methods vary by platform. For example, WhatsApp integration often utilizes the Baileys library, while Telegram relies on the grammY framework. iMessage integration is more complex, frequently requiring the use of a CLI tool or a dedicated macOS app to bypass Apple's sandboxing restrictions.
Technical Specifications
Moltbot is designed for technical users and developers who prioritize data sovereignty and local control. As an open-source project, it places the responsibility for maintenance and security squarely on the operator.
Runtime and Development Environment
The core codebase is primarily written in TypeScript (80.2%), reflecting its reliance on the modern JavaScript ecosystem for managing asynchronous events and WebSocket communication. Swift (13.2%) and Kotlin (1.8%) are utilized for the native components on macOS/iOS and Android, respectively.
| Technical Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Minimum Runtime | Node.js ≥ 22 |
| Preferred Package Manager | pnpm (npm and bun also supported) |
| Supported OS | macOS, Linux, Windows (via WSL2) |
| Primary Language | TypeScript |
| Database | SQLite (with optional sqlite-vec for vectors) |
The installation process typically involves a CLI-driven wizard (moltbot onboard) that handles the deployment of the Gateway daemon through launchd on macOS or systemd on Linux. For developers, the project supports a "gateway:watch" mode that allows for auto-reloading during TypeScript development.
Model Selection and Provider Configuration
While the "brain" of Moltbot can be any Large Language Model, the community has converged around Anthropic's Claude 3.5/4.5 series, specifically the Opus and Sonnet models, due to their superior long-context reasoning and tool-calling reliability.
Memory and Personal Context

The defining feature that distinguishes Moltbot from traditional chatbots is its treatment of memory. Traditional web-based LLMs lose context as soon as a session expires or reaches a token limit. Moltbot, conversely, utilizes a "local-first" memory harness that stores conversation history, metadata, and learned preferences as accessible Markdown files on the host machine.
Markdown-Based Reasoning and Retrieval
By storing memory in Markdown and utilizing SQLite for indexing, the assistant can perform sophisticated retrieval tasks. For instance, a user can refer to a casual comment made two weeks prior, and the assistant can locate that specific data point to inform a current task. This persistence allows the bot to become increasingly personalized over time, essentially learning the user's "operating system" for work and life.
Vector Acceleration (New in 2026)
Recent updates have introduced experimental session transcript indexing and sqlite-vec vector acceleration, allowing for more efficient semantic search across vast amounts of stored data. This ensures that as the user's local knowledge base grows—potentially containing years of project notes and email summaries—the assistant remains responsive and accurate.
Proactive Agency and Scheduling
Beyond reactive chat, Moltbot is capable of proactive engagement. It utilizes a scheduling engine to "wake up" and perform checks independently of user input:
- Morning BriefingsThe assistant synthesizes your calendar, weather, news, and urgent emails into a summary sent before the workday begins.
- Event MonitoringTracking stock price fluctuations, GitHub issues, or flight status changes and notifying you the moment a specific trigger is met.
- Heartbeat RoutinesPeriodically checking the health of local systems or the status of long-running autonomous tasks.
The Skills Marketplace
Extensibility is provided through a plugin system called ClawdHub (MoltHub), where users can share and install "skills". A skill is defined using a standardized SKILL.md format—a Markdown-based runbook that specifies an ordered procedure for the AI to follow.
Lobster: The Deterministic Workflow Runtime
To ensure safety and reliability in multi-step automations, Moltbot incorporates "Lobster," a typed workflow shell. Lobster allows the assistant to run deterministic sequences with explicit approval gates. For example, a deployment skill might require the bot to check git status, run tests, and pause for a user's manual "OK" before pushing code to a production server.
This mitigates the risk of the LLM "hallucinating" a destructive command path by binding its agency to a human-auditable procedure.
| Automation Task | Implementation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Inbox Triage | Gmail API integration to filter and unsubscribe | Reduced noise; summarized daily priorities |
| Web Scraping | Chrome-like headers and Readability extraction | Instant competitive research or news tracking |
| System Ops | Shell access to manage Docker/VPS instances | Remote infrastructure management via text |
| Media Management | Apple Music or local file system integration | Hands-free media control on the go |
Key Features of Moltbot

"Personal OS" Concept
Unlike standard chatbots, Moltbot functions as a persistent agent that runs 24/7 on your local machine (Mac, Windows, or Linux). It's not just a chat window; it's a background process that lives in your system.
Action-Oriented Tools
It uses a set of tools to perform real-world tasks like managing emails, controlling browsers, executing shell commands, and accessing local files. It bridges the gap between text and action.
Omnichannel Access
You interact with it through everyday messaging apps like WhatsApp, Discord, Slack, iMessage, and Telegram. It meets you where you already communicate.
Privacy-Focused
It is self-hosted, meaning your data and conversation memory remain on your own hardware rather than a corporate cloud. You own the infrastructure.
Moltbot vs Legacy Clawdbot
While the core technology remains the same, the rebrand brought several improvements and clarifications. Here's what changed:
| Aspect | Clawdbot (Legacy) | Moltbot (Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Official Repository | ❌ Compromised (Scammers) | ✓ github.com/moltbot |
| Twitter/X Handle | ❌ @clawdbot (Scammers) | ✓ @moltbot |
| HTTP Security | ⚠️ HTTP allowed by default | ✓ HTTPS required by default |
| Control UI Auth | ⚠️ Token-only possible | ✓ Device identity required |
| Trademark Status | ❌ Anthropic dispute | ✓ Clear trademark |
The security improvements (HTTPS enforcement, device identity) were implemented specifically because of the vulnerabilities discovered in early Clawdbot deployments.
The Economics of Personal AI
The rise of Moltbot has had unexpected ripple effects on the hardware market. The "narrative" that a personal AI assistant requires a dedicated server has led to a significant surge in sales of Apple's Mac Mini, to the point where they have reportedly sold out in some regions.
The Mac Mini "Status Symbol"
While a Mac Mini is not strictly required—Moltbot can run on a $5/month VPS—it has become the "status symbol" of the DIY AI movement. The appeal lies in always-on reliability and seamless Apple ecosystem integration (iMessage, Apple Shortcuts, Apple Music).
Cost-Benefit Comparison
| Hosting Option | Monthly Cost | Accessibility | Privacy/Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Mac Mini | $0 (after hardware) | Requires always-on | Absolute |
| Hetzner VPS | ~$3.50 - $10.00 | 24/7 (High uptime) | High |
| AWS/EC2 | $20.00 - $150.00+ | Variable (Scalable) | Moderate |
Impact on the "AI Agent" Market
The existence of an open-source, highly capable agentic framework like Moltbot poses a direct threat to the emerging market for paid AI agents. If a single developer can build a "sovereign" assistant that replaces specialized tools for coding, email management, and marketing, the economic viability of niche "AI Employee" startups may be called into question.
This decentralization of AI capability allows individuals to "own" their intelligence rather than "renting" it from a platform.
Security Vulnerabilities (2026 Update)
January 2026 Security Advisory: Security researchers discovered hundreds of exposed Moltbot/Clawdbot control panels on the public internet due to misconfigurations. If you deployed before reading this, audit your setup immediately.
What Was Exposed?
- API Keys & Bot Tokens: Anthropic, OpenAI, Discord, Telegram credentials
- OAuth Secrets: Google, GitHub, and other integration secrets
- Full Conversation Histories: Private messages between users and their bots
- Configuration Data: System prompts, memory files, and personal preferences
In some critical instances, researchers found unauthenticated command execution on the host system, sometimes with elevated (root) privileges. An attacker could impersonate the bot operator, inject malicious instructions, or exfiltrate all files accessible to the Moltbot process.
How to Secure Your Instance
- Enforce HTTPSNever expose the control UI over plain HTTP. Use a reverse proxy with TLS.
- IP WhitelistingUse firewall rules to restrict access to known IP addresses only.
- Run Security AuditExecute
moltbot security audit --deepregularly. - Use Docker SandboxingIsolate Moltbot in a container with minimal filesystem access.
Security Analysis: Attack Surface
As a rapidly evolving open-source project, Moltbot has faced several technical security challenges. Recent versions have addressed specific CVEs, such as CVE-2025-59466 (Gateway DoS) and CVE-2026-21636 (Permission Bypass).
The Threat of Prompt Injection
Perhaps the most significant risk is not a code bug, but the inherent nature of natural language processing. Agentic systems that read untrusted content—such as emails or web search results—are vulnerable to "prompt injection".
An attacker can hide instructions in a web page or an email that, when read by Moltbot, trick the bot into performing malicious actions (e.g. exfiltrating data).
Safety and Security Warnings
SOCIAL MEDIA SECURITY ALERT
The Instagram and TikTok handles for "@clawdbot" are no longer controlled by the official developers.
During the transition to Moltbot, several legacy Clawdbot social media accounts were taken over by malicious actors. These accounts are currently being used to distribute "forked" versions of the bot that contain malware designed to exfiltrate private API keys.
Action Required: Only use official links from the Moltbot GitHub (github.com/moltbot). Avoid any "Clawdbot" downloads found on social media.
High-Level Access Risk: While popular, experts warn that Clawdbot/Moltbot requires high-level access to your computer. Granting an AI agent ability to read files and execute shell commands can create significant security risks.
| Risk Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Misconfiguration | Exposing the control port to the internet without auth. |
| Prompt Injection | Malicious websites or emails could trick the agent into executing harmful commands. |
| Data Leakage | Sensitive data in "memory" could be accessed if the database is not encrypted. |
Users should treat Moltbot like a root-access user on their system. Only install it on machines where you understand the security implications, and consider running it in a sandboxed environment (like Docker) if possible.
Moltbot vs Other AI Systems
Moltbot vs Corporate Assistants
While Apple's Gemini-powered Siri or Google Assistant focus on a polished, consumer-safe experience, they lack the ability to run arbitrary shell scripts or access the raw file system—features that define the Moltbot experience. Corporate assistants are bound by strict safety guidelines that prevent high-stakes automations.
Moltbot vs Paid Agent Platforms
| Platform | Ownership | Interface | Core Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moltbot | Open Source | Messaging Gateway | Local Execution / Customization |
| Poke | SaaS | SMS / WhatsApp | Ease of Use / No Setup |
| Claude Code | Proprietary | CLI | Optimized Coding |
| Benev.ai | SaaS | Messaging Apps | Consumer Accessibility |
Strategic Outlook
The Rise of the "Personal Stack"
The industry is witnessing the emergence of a "personal AI stack," where the individual owns the gateway, the memory, and the orchestration, while "renting" the intelligence from model providers via API. This model aligns with digital minimalism and decentralization trends.
The Impending "Bot vs. Bot" Era
"As agentic systems like Moltbot become more common, the digital landscape will shift from human-to-human interaction to agent-to-agent negotiation."
The strategic challenge moving forward will be ensuring that as digital butlers are granted the keys to digital homes, it is done with a clear understanding of the architectural and security responsibilities that sovereignty demands.
What People Say
"It's the fact that clawd can just keep building upon itself just by talking to it in discord is crazy. The future is already here."
"Using @moltbot for a week and it genuinely feels like early AGI. The gap between 'imagination' and 'execution' has disappeared."
"This nukes SaaS startups. A hackable, on-prem personal employee is the ultimate end-game for productivity."
"Why @moltbot is nuts: your context and skills live on YOUR computer, not a walled garden... Only 19 days old and constantly improving."
"A smart model with eyes and hands at a desk with keyboard and mouse. You message it like a coworker and it does everything a person could do with that Mac mini."
"Just told Ema, my @moltbot, via Telegram to turn off the PC (and herself, as she was running on it) Executed perfectly. Such a cool tool"
Our Take: The Editorial View
Greg's Analysis
Moltbot (né Clawdbot) is perhaps the most interesting "shadow utility" in the current AI landscape. While Anthropic's Claude is officially a productivity-first tool, Moltbot turns it into a personal concierge that lives on your machine. The viral success of this project—despite the multiple cease-and-desist rebrands—highlights a massive demand for AI that acts on your behalf rather than just talking to you.
Is it safe? If you use the official source, it's about as safe as any local script running an LLM. However, the compromise of their old social media handles is a classic example of why "agentic AI" needs careful management. One wrong download and you've given a bot the keys to your machine.
The bottom line: Moltbot is a great preview of what "local agency" looks like, but its fragile legal standing means it's for power users and experimenters, not for mission-critical business systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Verified for Moltbot v4.5 Update (Jan 2026)